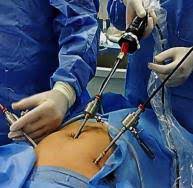
Appendicectomy
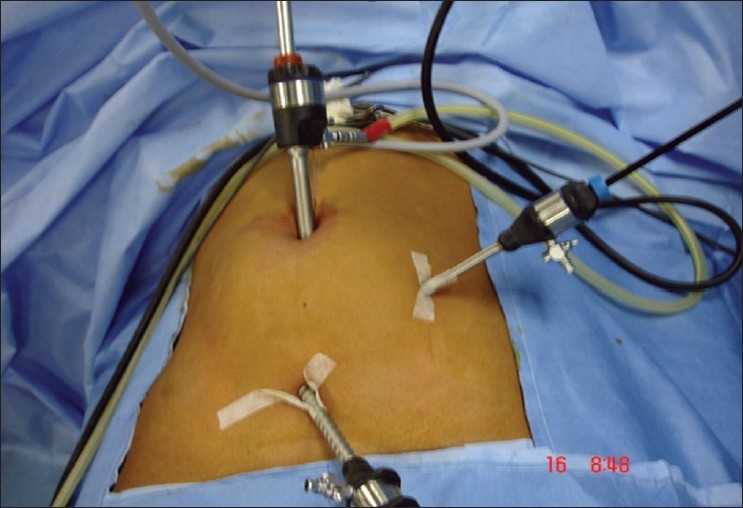
What is an Appendectomy?
An appendectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the appendix, a small pouch-like organ located at the junction of the small and large intestines.
The appendix is prone to inflammation, a condition known as appendicitis, which requires prompt surgical intervention to prevent complications.
Types of Appendectomy:
Open Appendectomy: This traditional surgical approach involves making an incision in the lower right abdomen to access and remove the appendix. Open appendectomy may be recommended in cases of severe inflammation or if laparoscopic surgery is not feasible.
Laparoscopic Appendectomy: This minimally invasive procedure is the preferred method for most cases of appendicitis. It involves making several small incisions in the abdomen and using a tiny camera and surgical instruments to remove the appendix.