Gastrointestinal Care

Gastric ulcer
A gastric ulcer is a sore or lesion that develops in the lining of the stomach. It’s often caused by the erosion of the protective lining due to factors like infection with H. pylori bacteria, long-term use of NSAIDs, excessive alcohol consumption, or stress. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and in severe cases, bleeding or perforation.
Treatment involves medication to reduce stomach acid production, antibiotics to treat H. pylori infection if present, and lifestyle modifications.
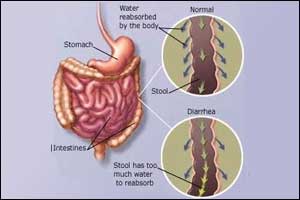
Chronic Diarrhea
Chronic diarrhea is defined as frequent, loose, or watery stools lasting for more than four weeks. It can be caused by various factors, including infections, inflammatory bowel diseases (such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis), food intolerances, medications, or digestive disorders. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, cramping, dehydration, and weight loss.
Treatment aims to address the underlying cause, which may include medication, dietary changes, probiotics, or lifestyle modifications.
Heartburn
Heartburn, or acid indigestion, is a burning sensation in the chest that occurs when stomach acid backs up into the esophagus. It’s often triggered by factors like overeating, eating spicy or fatty foods, lying down after eating, or pregnancy. Symptoms may worsen when bending over or lying down and may be accompanied by regurgitation, a sour taste in the mouth, or difficulty swallowing. Treatment typically involves lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals, raising the head of the bed, and over-the-counter antacids or acid reducers.
If symptoms persist, further evaluation by a healthcare professional may be needed to rule out underlying conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
