Hernia surgery
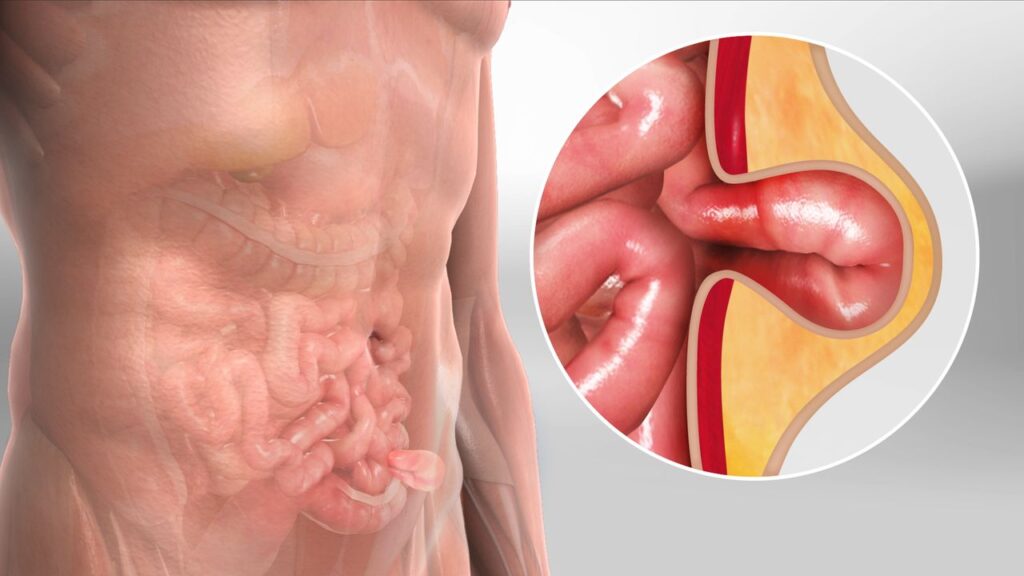
What is Hernia Surgery?
Hernia surgery, also known as herniorrhaphy or hernioplasty, is a surgical procedure to repair a hernia. A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot or tear in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue.
Hernias can occur in various body parts, including the abdomen, groin, and upper thigh.
Types of Hernia Surgery:
Open Hernia Repair: This traditional surgical approach involves making an incision directly over the hernia site to access and repair the hernia. Open hernia repair may be recommended for larger hernias or in cases where laparoscopic surgery is not feasible.
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: This minimally invasive procedure involves making several small incisions in the abdomen and using a tiny camera and surgical instruments to repair the hernia. Laparoscopic hernia repair offers advantages such as shorter recovery time and reduced risk of complications.
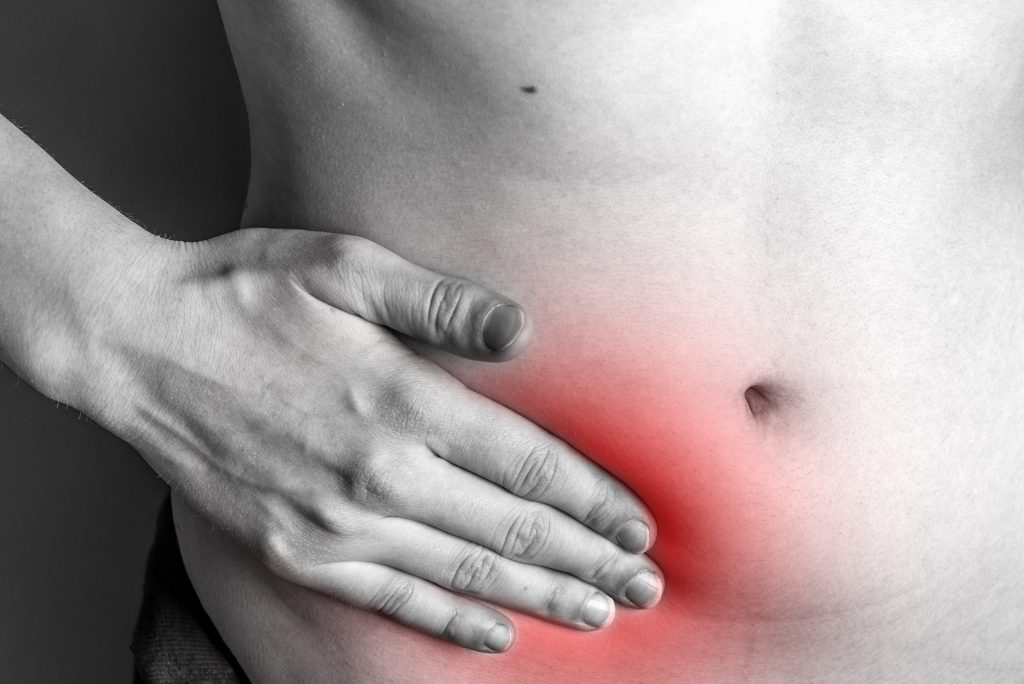
Why is Hernia Surgery Performed?
Hernia surgery is performed to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications associated with hernias, including pain, discomfort, and the risk of strangulation or incarceration (when the herniated tissue becomes trapped and blood flow is compromised).
Common types of hernias that may require surgery include inguinal hernias, umbilical hernias, and incisional hernias.
